NCX1 rabbit pAb - 50 μL
In cardiac myocytes, Ca (2+) concentrations alternate between high levels during contraction and low levels during relaxation. The increase in Ca (2+) concentration during contraction is primarily due to release of Ca (2+) from intracellular stores. However, some Ca (2+) also enters the cell through the sarcolemma (plasma membrane). During relaxation, Ca (2+) is sequestered within the intracellular stores. To prevent overloading of intracellular stores, the Ca (2+) that entered across the sarcolemma must be extruded from the cell. The Na (+)-Ca (2+) exchanger is the primary mechanism by which the Ca (2+) is extruded from the cell during relaxation. In the heart, the exchanger may play a key role in digitalis action. The exchanger is the dominant mechanism in returning the cardiac myocyte to its resting state following excitation. [supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004],
Distributed by Gentaur
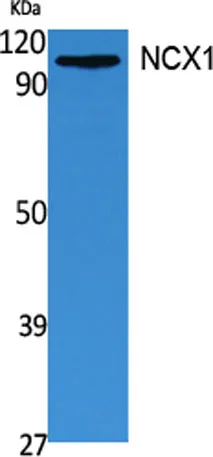
View the Technical Datasheet of the product below

View the Technical Datasheet of the product below
Votre snippet dynamique sera affiché ici... Ce message est affiché parce que vous n'avez pas défini le filtre et le modèle à utiliser.